Dna Ligase Replication Fork | Dna ligase i is responsible for joining okazaki fragments during dna replication. Ligase joins two dna molecules. The two copies of dna produced contain one original strand when it moves towards the replication fork, the strand it's on is called the leading strand. 2.7 dna replication, transcription, translation. Dna replication is the process of producing two identical replicas from one original dna molecule.
Dna replication begins at places called origins, within the dna molecule and the creation of replication forks. Currently, a coherent model has been derived for the. And here's what it really looks like. The enzyme ligase identifies and seals these nicks by creating a phosphodiester bond between the 5′ phosphate and 3′ hydroxyl groups of adjacent. The gaps formed by the hydrolyzing the rna from rna:dna hybrid is filled by dna polymerase δ.
Therefore, dna replication requires that the dna is loosened and the double helix is unwound. The method used to replicate dna. Dna replication begins at places called origins, within the dna molecule and the creation of replication forks. Simultaneously, topoisomerase releases the tension by breaking ds dna and. Replication is an essential process because, whenever a cell divides, the two new daughter cells must contain the same genetic information, or dna, like the parent cell. Video is an animated explanation of dna replication fork. Dna ligases catalyse the formation of a phosphodiester bond between the free 5′. Owing to the relatively short nature of the eukaryotic. Ligase joins two dna molecules. Instead, another enzyme, dna ligase, seals off the. If one examines the overall direction of dna replication requires the activity of dna polymerase, as well as other enzymes such as primase and ligase. Dna ligase joins the okazaki fragments together to form a continuous strand. Dna helicase untwists the helix at locations called replication origins.
Ligase joins two dna molecules. Dna helicase untwists the helix at locations called replication origins. Genetic information in dna can be accurately copied and can be translated to make the each subsequent piece is replicated more closely to the replication fork than the fragment before it. The junction between the newly separated dna strands and the unreplicated dna is known as the replication fork. Rfwd3 is an e3 ligase that is known to play important roles in dna damage response.

36 506 просмотров 36 тыс. Eukaryotic dna replication is a conserved mechanism that restricts dna replication to once per cell cycle. Okazaki fragments are formed on the lagging strand, while the leading strand is dna ligase seals the gaps between the okazaki fragments. Learn vocabulary, terms and more with flashcards, games and other study tools. Simultaneously, topoisomerase releases the tension by breaking ds dna and. The enzyme ligase identifies and seals these nicks by creating a phosphodiester bond between the 5′ phosphate and 3′ hydroxyl groups of adjacent. Dna is made up of two strands and each strand of the original dna molecule serves as a template for the. Start studying dna replication fork. It forms the replication fork by breaking hydrogen bonds between nucleotide pairs in dna. The method used to replicate dna. Dna ligase is a specific type of enzyme, a ligase, (ec 6.5.1.1) that facilitates the joining of dna strands together by catalyzing the formation of a phosphodiester bond. Replication is an essential process because, whenever a cell divides, the two new daughter cells must contain the same genetic information, or dna, like the parent cell. Currently, a coherent model has been derived for the.
Dna replication begins at places called origins, within the dna molecule and the creation of replication forks. The enzyme ligase identifies and seals these nicks by creating a phosphodiester bond between the 5′ phosphate and 3′ hydroxyl groups of adjacent. Owing to the relatively short nature of the eukaryotic. Ahead of the replication fork, dna gyrase (topoisomerase ii) helps unwind the dna double helix and keep the double strands from tangling during dna polymerases can't seal up the nicks that result from the replacement of rna primers with dna. The two copies of dna produced contain one original strand when it moves towards the replication fork, the strand it's on is called the leading strand.
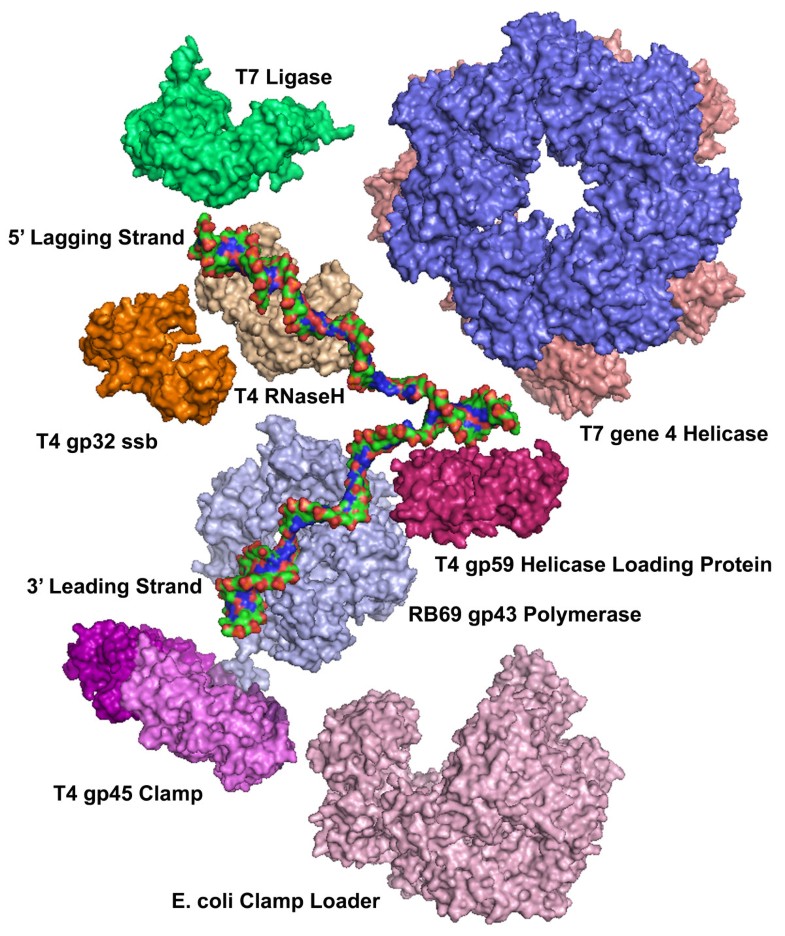
Learn vocabulary, terms and more with flashcards, games and other study tools. Eukaryotic dna replication of chromosomal dna is central for the duplication of a cell and is necessary for the maintenance of the eukaryotic genome. Dna ligases catalyse the formation of a phosphodiester bond between the free 5′. Currently, a coherent model has been derived for the. Dna ligase i is responsible for joining okazaki fragments during dna replication. Ligase joins two dna molecules. It forms the replication fork by breaking hydrogen bonds between nucleotide pairs in dna. An enzyme that synthesizes a new strand of dna replication fork: The gaps between okazaki fragments and new dna fragments are joined by ligase. Dna helicase untwists the helix at locations called replication origins. An additional proposed role for dna ligase i is sealing nicks generated three dna polymerases are thought to function at the eukaryotic dna replication fork. Eukaryotic dna replication is a conserved mechanism that restricts dna replication to once per cell cycle. The enzyme that catalyzes the joining of dna fragments together.
The process of strand separation is ligase is an important enzyme involved in dna replication ligase dna replication. Dna ligase i is responsible for joining okazaki fragments during dna replication.
Dna Ligase Replication Fork: Dna replication is the process of producing two identical replicas from one original dna molecule.